Menu
MetalsTek Engineering holds a large inventory of Antimony Metals, including its powder, pieces, ingots. We can ship your order within short time and competitive prices.

Material: Antimony, CAS# 7440-36-0
Purity: 99.7%~99.999%
Properties: 6.7g/cc Density, 630.63°C/1,167.13°F M.P., 24.4 W/(m⋅K) Thermal Conductivity
Shape: Powder, Spherical Powder
Sizes: 50nm~3μm
Antimony metal powder is widely used in the semiconductor industry to produce infrared detectors, diodes, and hall-effect devices. It is also used as an alloy to increase the hardness and strength of lead, which is commonly used in storage batteries. In addition to industrial applications, antimony is used for cosmetic purposes, such as darkening the brows and lashes, or as an eye liner. It also has significant applications in print and pigment industries.

Material: Antimony, CAS# 7440-36-0
Purity: 99.9%
Properties: 6.7g/cc Density, 630.63°C/1,167.13°F M.P.
Shape: Powder, Spherical Powder
Sizes: 50nm, 1~3μm

Material: Antimony, CAS# 7440-36-0
Purity: 99.7%~99.99999%
Properties: 6.7g/cc Density, 630.63°C/1,167.13°F M.P., 24.4 W/(m⋅K) Thermal Conductivity
Shape: Pieces, Chunks, Ingots
Sizes: Tailored Size
Item No. | Description | Purity |
Sb-2N65 | Antimony Metal Ingot | 99.65%, Pb < 0.30%, As < 0.10%, Fe < 0.03% |
Sb-2N85 | Antimony Metal Ingot | 99.85%, Pb < 0.10%, As < 0.05%, Fe < 0.02% |
Sb-2N | Antimony Metal Ingot | 99.90% |
Sb-R82 | High Lead-Antimony Metal Ingot | Sb: 88-93%, Pb: 6-10%, As < 0.8%, Cu < 0.2%, Fe < 0.25%, S < 0.2 |
Sb-5N | Antimony Metal (Ingot, powder, lump, particle) For semiconductor applications; | 99.999% |
Sb-6N | Antimony Metal (Ingot, powder, lump, particle) For semiconductor applications; | 99.9999% |
Sb-7N | Antimony Metal (Ingot, powder, lump, particle) For semiconductor applications; | 99.99999% |
Antimony is a unique semimetal with atomic number 51 in the periodic table. It has several distinctive properties, including low thermal conductivity, high electrical resistance, and a bluish-white metallic luster. Antimony plays a vital role in various industries due to its industrial and chemical applications. It is widely used in flame retardants, batteries, semiconductors, and alloys. Antimony’s exceptional properties make it particularly valuable in the production of lead-acid batteries, where it improves the battery’s durability and performance. It is also used in semiconductor manufacturing, where it acts as a dopant to modify the electrical properties of silicon. Additionally, its use in alloys improves the mechanical properties of metals, making them more resistant to corrosion and wear. Despite its toxicity, careful handling and responsible management ensure its safe and effective utilization across various industrial sectors, highlighting its significance in modern technology and materials science.
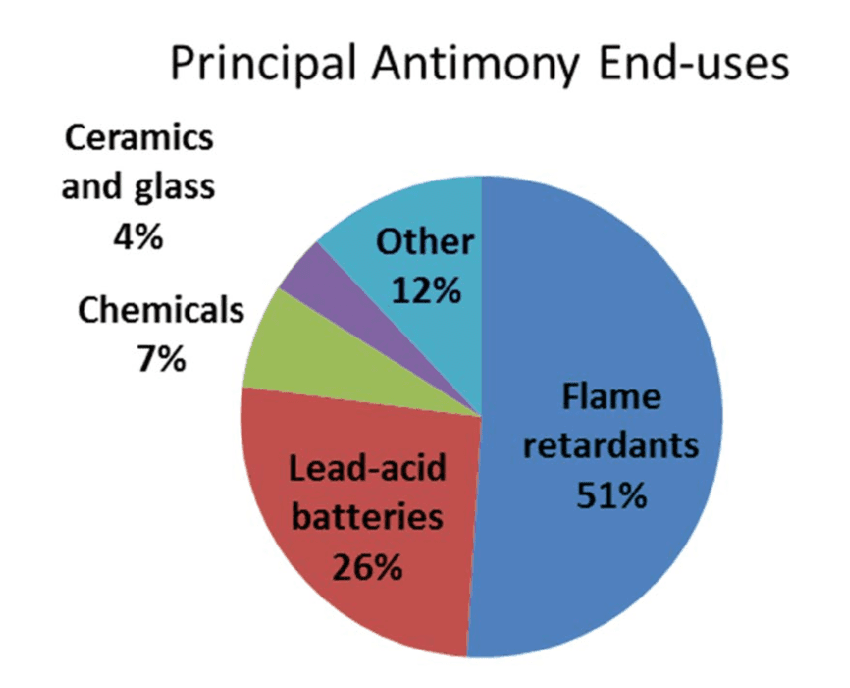
Antimony Metal finds applications across various industries due to its unique properties and versatile nature. Some key applications include:
Our Antimony Metals are clearly labeled externally to ensure efficient identification and quality control. We take great care to prevent any damage during storage or transportation.