Menu
MetalsTek Engineering offers tungsten filaments in various shapes and wire counts. Select a heater shape that closely matches the size of your substrate and the properties or shape of the material you want to heat.
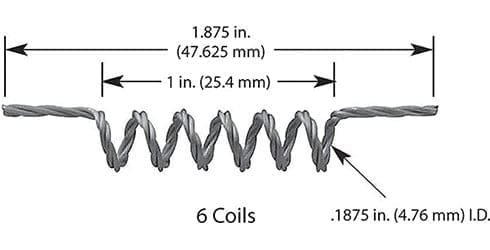
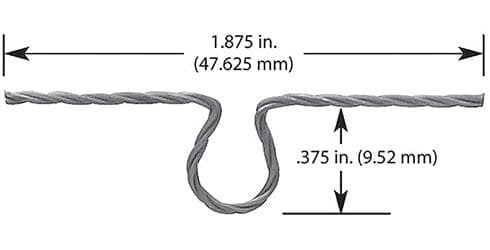
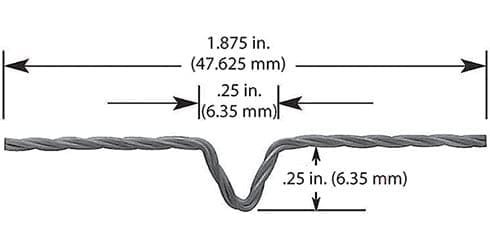
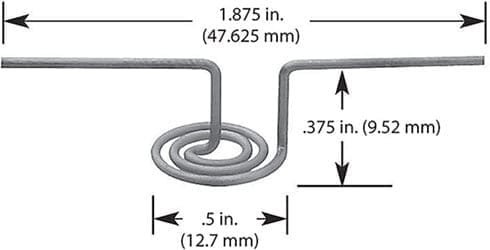

#001: 1 Wire * Diameter 0.762mm / 0.03″
#002: 3 Wires * Diameter 0.635mm / 0.025″
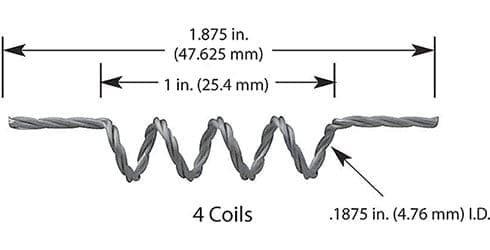
#003: 1 Wire * Diameter 0.762mm / 0.03″
#004: 3 Wires * Diameter 0.635mm / 0.025″
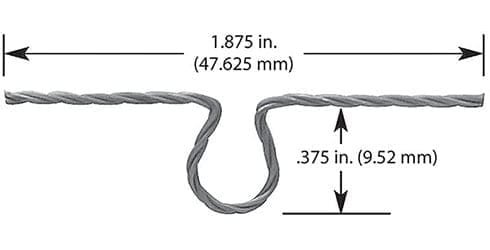
#005: 1 Wire * Diameter 0.762mm / 0.03″
#006: 3 Wires * Diameter 0.635mm / 0.025″

#007: 1 Wire * Diameter 0.762mm / 0.03″
#008: 3 Wires * Diameter 0.635mm / 0.025″
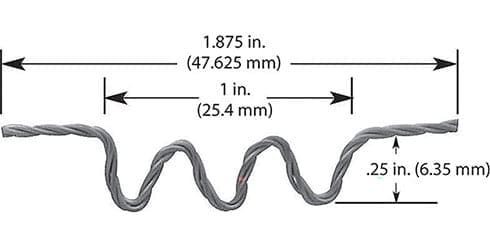
#009: 1 Wire * Diameter 0.762mm / 0.03″
#010: 3 Wires * Diameter 0.635mm / 0.025″

#011: 1 Wire * Diameter 0.762mm / 0.03″
#012: 3 Wires * Diameter 1.000mm / 0.04″
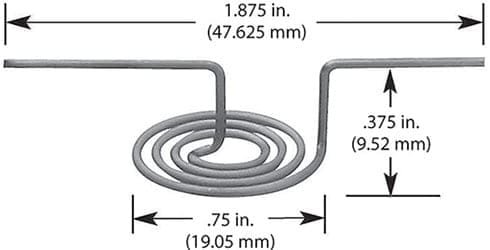
#013: 1 Wire * Diameter 0.762mm / 0.03″
#014: 3 Wires * Diameter 1.000mm / 0.04″
Tungsten filaments are commonly used in high vacuum thin film deposition systems to heat substrates or crucibles containing the material to be deposited. The choice of filament shape and number of wires depends on the substrate’s area requirements and the characteristics of the material being heated.
Some key considerations when selecting a tungsten filament:
In summary, choosing the right tungsten filament involves balancing factors like cost, size, heating uniformity and lifetime to match the specific requirements of the deposition process and substrate. Consulting with the filament manufacturer can help select the optimal configuration.
MetalsTek has rich experience in customizing micron-electronic filaments, with short lead times and competitive pricing.