Menu
MetalsTek Engineering’s dedication to excellence extends to our Lead Sheets and Foils, setting a benchmark for quality and reliability in the industry.

Material: Lead
Purity: Pb 99.99% Min.
Form: Sheet, Foil, Plate
Standard Thickness: 0.5mm, 0.6mm, 0.8mm, 1mm, 1.5mm, 1.8mm, 2mm, 2.5mm, 3mm, 4mm, 5mm, 6mm, 7mm, 8mm, 10mm
Size: Width≤2,000mm; Length- Free Cut for Rolled Sheet, ≤2,000mm for thickness over 3mm

Material: Lead
Purity: Pb 99.99% Min.
Form: Foil, Sheet, Plate
Thickness: 1mm, 1.5mm, 1.8mm, 2mm, 2.5mm, 3mm, 4mm, 5mm, 6mm, 7mm, 8mm, 10mm
Size: Width≤2,000mm; Length- Free Cut for Rolled Sheet, ≤2,000mm for thickness over 3mm
Material: Lead
Purity: Pb 99.99% Min.
Form: Plate, Bar
Size: ≤70mm * Width≤2,000mm * Length- Free Cut

Material: Lead
Purity: Pb 99.99% Min.
Form: Flat Bricks, Interlocking Bricks, Coated Lead Bricks
Size: Customized Sizes

Material: Lead
Purity: Pb 99.99% Min.
Shape: Discs, Rings, Irregular Shapes, or Per Drawing
Size: Tailored Sizes
Lead Sheets and Foils are thin, malleable sheets made from lead metal, known for their versatility and unique properties. Typically produced through a rolling process, these sheets exhibit high ductility and can be easily manipulated into different shapes and sizes, making them ideal for a wide range of applications across industries. Lead Sheets and Foils find extensive use in radiation shielding applications due to lead’s exceptional ability to absorb and block radiation. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. *Cited from Wikipedia
In medical facilities, Lead Sheets and Foils are utilized to construct protective barriers in X-ray rooms, CT scan rooms, and nuclear medicine facilities, ensuring the safety of patients, medical personnel, and the public from harmful radiation exposure. Moreover, Lead Sheets and Foils are employed in the manufacturing of radiation shielding equipment such as lead aprons, vests, and curtains, providing essential protection during medical procedures.
In addition to their role in radiation shielding, Lead Sheets and Foils are also utilized in diverse industrial applications. They serve as effective barriers against corrosion, making them valuable in the construction of chemical storage containers, pipes, and linings for tanks handling corrosive substances. Furthermore, Lead Sheets and Foils find applications in the automotive industry for soundproofing and vibration dampening purposes, enhancing the comfort and performance of vehicles. Other applications include roofing materials, art and craft projects, and counterweights for various machinery and equipment. Overall, Lead Sheets and Foils offer exceptional versatility and functionality, making them indispensable in numerous industrial sectors.

Lead Sheet and Plate play a crucial role in providing radiation shielding, soundproofing, and protection against chemical corrosion. Its applications range from lining walls in medical facilities to creating protective barriers in nuclear power plants. This material is essential for ensuring safety, durability, and efficiency in diverse industrial and construction settings.
Our Lead Sheets and Plates are clearly labeled externally to ensure efficient identification and quality control. We take great care to prevent any damage during storage or transportation.
Are you looking to enhance safety and protect against the harmful effects of radiation? Look no further. In this article, we delve into the world of lead in radioshielding and how it can be mastered to provide unparalleled protection. With the constant advancement of technology, radiation exposure has become a pressing concern in various industries. From healthcare to nuclear power plants, it is crucial to have effective shielding solutions that prioritize safety without compromising on performance. Our cutting-edge solutions are designed to meet the highest standards of radiation protection. By utilizing the unique properties of lead, we provide innovative solutions that not only shield against radiation but also optimize efficiency. Our expert team combines their extensive knowledge with state-of-the-art technology to deliver comprehensive radioshielding solutions tailored to your specific needs. Join us as we explore the latest advancements in radioshielding and how our solutions can help you achieve optimal safety. With our lead-based solutions, you can master radioshielding and stay ahead in safeguarding your assets, employees, and the environment. Get ready to experience enhanced protection like never before.
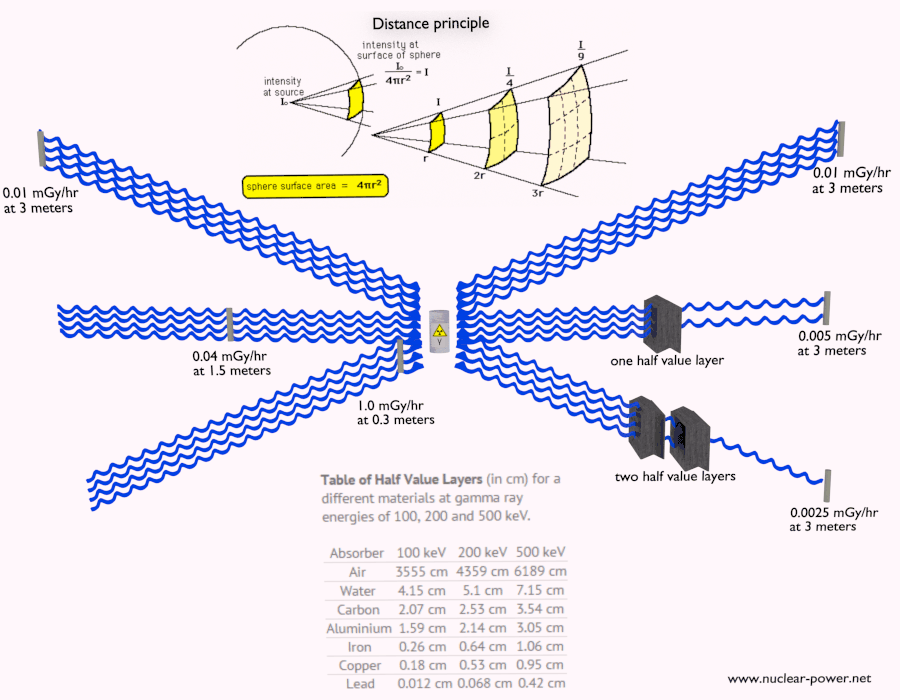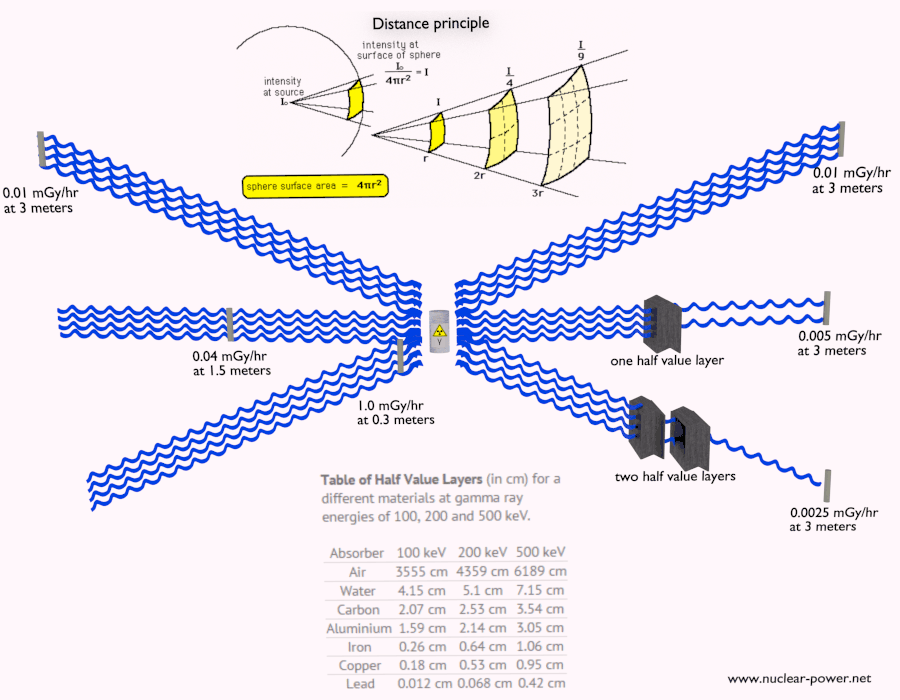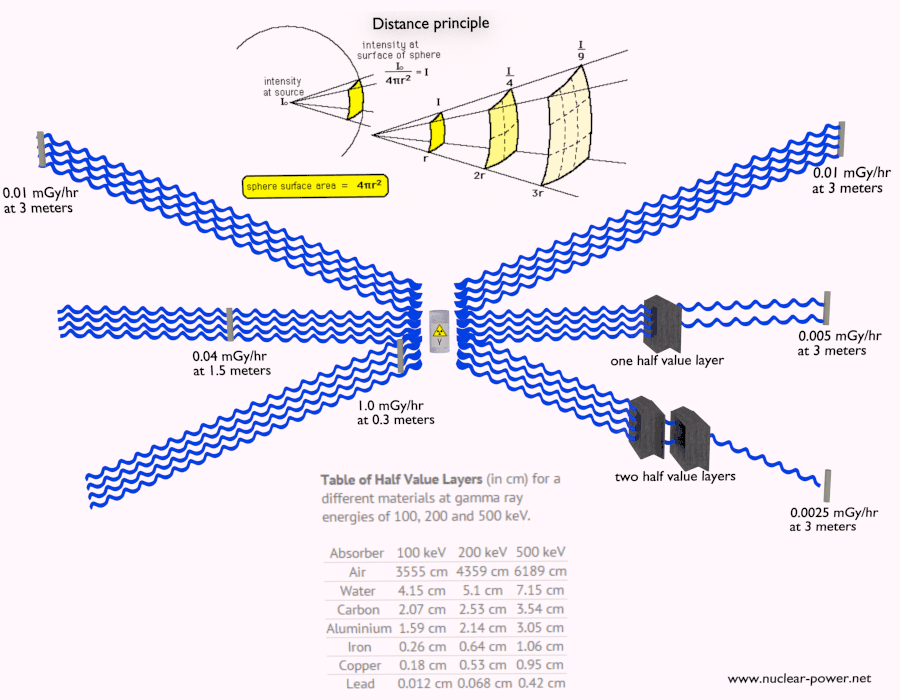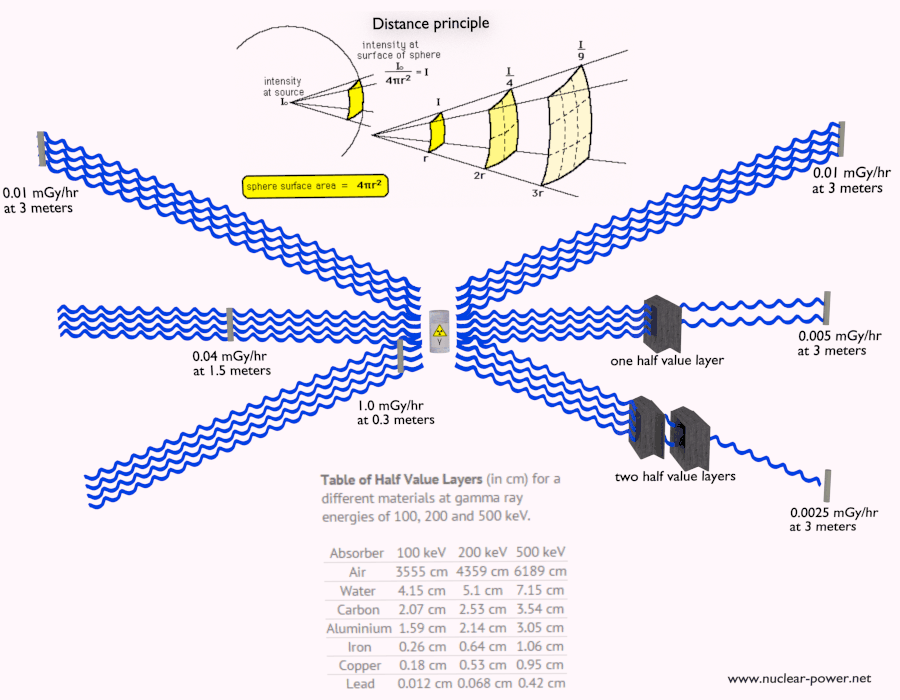
Lead is an effective material for shielding against various types of radiation, particularly gamma rays and X-rays, due to its high density and high atomic number. Here are the key points about the role of lead in radio shielding:
Attenuation of Gamma and X-rays
Shielding Applications

Lead is an effective material for radio shielding, particularly against gamma rays and X-rays, due to the following key properties:
High Density
High Atomic Number
Stable Isotopes
Malleability and Workability
Cost-Effectiveness
Lead’s unique combination of high density, high atomic number, stable isotopes, malleability, and cost-effectiveness make it an ideal material for effectively shielding against harmful gamma rays and X-rays in various industrial, medical, and scientific settings.

Throughout its history, lead’s unique properties have made it an invaluable material for radio shielding, protecting individuals and equipment from the harmful effects of ionizing radiation in medical, industrial, and scientific settings.
Early Discoveries and Applications
Widespread Adoption in Medical and Industrial Settings
Continued Use and Advancements
There has been growing interest in developing alternatives to lead for radio shielding applications, particularly due to concerns over lead’s toxicity. Some promising lead-free materials and their properties are:
Metal-Polymer Composites
Metal-impregnated polymers, such as tungsten or bismuth composites, offer effective shielding against gamma and X-ray radiation. These materials combine the shielding properties of high-density metals with the flexibility and lightweight nature of polymers.
Barium Sulfate and Metal Oxide Composites
Researchers have explored using barium sulfate (BaSO4) and metal oxides like magnesium oxide (MgO) as fillers in polymer matrices to create lead-free shielding materials.
Polyaniline-Based Composites
Polyaniline (PANI), a conductive polymer, has been explored in combination with other materials for electromagnetic shielding applications.
While lead remains a widely used and cost-effective option for radio shielding, these alternative materials offer potential solutions to address concerns over lead’s toxicity while providing effective shielding capabilities. Ongoing research aims to optimize the performance, cost, and manufacturing processes of these lead-free alternatives for various shielding applications.
Lead offers several key benefits that make it an effective and widely used material for radio shielding, particularly against gamma rays and X-rays:
High Density and Atomic Number
Stable Isotopes
Malleability and Workability
Cost-Effectiveness
Proven Effectiveness
While lead is not effective against all types of radiation (e.g., high-energy electrons and neutrons), its unique combination of properties makes it an ideal material for shielding against harmful gamma rays and X-rays, offering reliable protection while being economical and versatile.
Working with lead for radio shielding applications requires adherence to various regulations and safety considerations due to the toxic nature of lead. Here are some key points regarding regulations and safety measures:
Regulations
Safety Considerations
Strict adherence to regulations and safety protocols is vital when working with lead for radio shielding applications. Employers and workers must prioritize the implementation of engineering controls, administrative controls, and the use of appropriate PPE to minimize the risks associated with lead exposure and ensure a safe working environment.
Lead recycling and sustainability are important considerations in the use of lead for radio shielding applications. Here are some key points regarding lead recycling and sustainability efforts:
Lead Recycling
Sustainability Initiatives
Regulatory Compliance
By prioritizing lead recycling and implementing sustainable practices, radiation shielding manufacturers and users can contribute to a more environmentally responsible industry while ensuring the continued availability and effectiveness of lead shielding solutions.

Numerous case studies highlight lead’s effectiveness in radio shielding. Here are a few case studies that showcase the effectiveness of lead in radio shielding applications:
Medical Imaging
A study published in the Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics evaluated the shielding effectiveness of lead aprons used in interventional radiology procedures. The researchers found that 0.5 mm lead-equivalent aprons provided an average shielding factor of 63.9%, effectively reducing the radiation dose to the operator’s body.
Nuclear Power Plants
Lead shielding plays a crucial role in nuclear power plants, protecting workers and equipment from harmful radiation. A case study by the Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI) highlighted the use of lead bricks and panels for shielding in various areas of a nuclear plant, including the reactor containment building, spent fuel pool, and radioactive waste storage facilities. The lead shielding effectively reduced radiation levels, ensuring safe working conditions.
Industrial Radiography
In the field of industrial radiography, where high-energy X-rays and gamma rays are used for non-destructive testing, lead shielding is essential. A case study by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) demonstrated the use of lead-lined cabinets and containers for storing and transporting radioactive sources. The lead shielding effectively contained the radiation, minimizing exposure to personnel and the environment.
Scientific Research
Lead shielding is widely used in scientific research facilities, such as particle accelerators and radiation laboratories. A case study by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) described the use of lead bricks and panels to construct shielded enclosures for experiments involving high-energy particle beams. The lead shielding effectively attenuated the radiation, allowing researchers to work safely in close proximity to the experiments.
These case studies highlight the effectiveness of lead in shielding against various types of ionizing radiation, including X-rays, gamma rays, and high-energy particle beams. Lead’s unique properties, such as high density and high atomic number, make it an indispensable material for radiation shielding in diverse applications, ensuring the safety of personnel, equipment, and the environment.
The future of lead in radio shielding remains promising, despite the exploration of alternative materials. Lead’s unique properties, including its high density, high atomic number, and cost-effectiveness, make it an ideal material for shielding against gamma rays and X-rays. However, there is a growing emphasis on addressing concerns related to lead’s toxicity and exploring more sustainable solutions.Here are some key points regarding the future of lead in radio shielding:
While lead alternatives are being explored, lead’s unique properties and proven effectiveness in radio shielding applications will likely ensure its continued use in the foreseeable future. However, the industry will need to strike a balance between leveraging lead’s advantages and addressing concerns over its toxicity through responsible handling, recycling, and the adoption of sustainable practices.