Menu
MetalsTek Engineering holds a large inventory of Cobalt Metals and Cobalt products. Our ready-to-ship products can save you time and costs on production and the R&D process.

Material: Cobalt Pellets
Purity: Co 99.98% (In Stock)
Properties: 8.9g/cc Density, 1,495°C M.P.
Thermal Conductivity: 100 W/m.K
Form: Pellets, or Customized
Size: 3*3mm, 6*6mm, 14.5*0.2mm, 10*10*2mm, or Tailored Size

Material: Cobalt
Purity: Co 99.98% (In Stock)
Properties: 8.9g/cc Density, 1,495°C M.P.
Form: Flakes, Ingots, Chunks
Thickness: 0.05~8mm
Size: Irregular Sizes, or Tailored Size
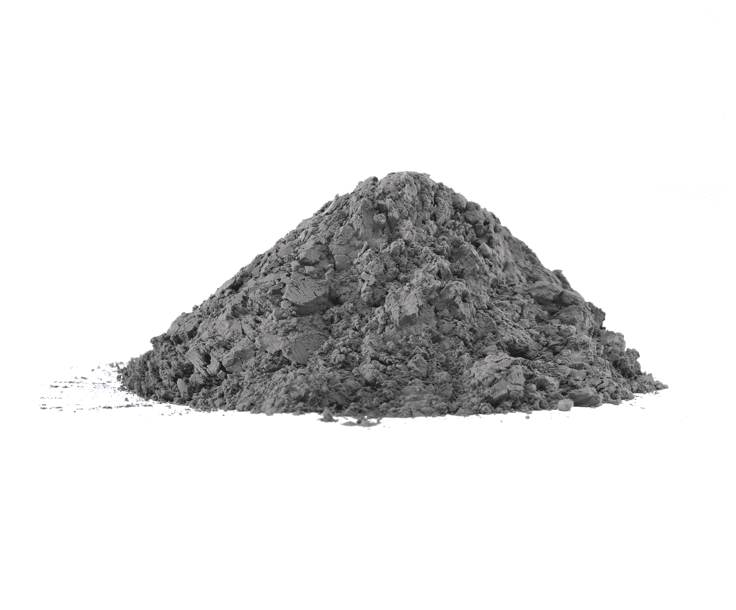

Material: Cobalt
Purity: Co 99.98% (In Stock)
Properties: 8.9g/cc Density, 1,495°C M.P.
Thermal Conductivity: 100 W/m.K
Form: Micro Powder, Nano Powder, Spherical Powder
Size: Varies, Can be Customized

Material: Al-10Co
Purity: 99.99% / Tailored Compositions
Form: Ingot
Price for Reference: $41.00 / KG **(May Varies)
Cobalt Metal is a lustrous, hard, silver-gray metal with unique properties that make it valuable in various industrial applications. It is often found in combination with other metals in ores, such as cobaltite, but it can also be produced as a by-product of nickel and copper mining. Cobalt Metal is known for its high melting point, excellent magnetic properties, and corrosion resistance. These characteristics make it particularly useful in producing alloys, including high-strength alloys used in aerospace components, superalloys for gas turbine engines, and magnetic alloys for electrical and electronic applications.
Additionally, Cobalt Metal is used to manufacture rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, which improve battery performance and stability. Due to its versatility and unique properties, cobalt metal is crucial in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and healthcare.
Cobalt Metals find various applications across various industries due to their unique properties. Some typical applications of cobalt metals include:
1. Aerospace and Aviation: Cobalt-based superalloys are used in aircraft engines and gas turbines due to their high-temperature strength, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance.
2. Medical Devices: Cobalt-chromium alloys are utilized in orthopedic implants, such as artificial hip and knee joints, due to their biocompatibility, strength, and wear resistance.
3. Electronics: Due to its magnetic properties, cobalt produces magnetic alloys for electrical components like hard disk drives, magnetic sensors, and transformers.
4. Rechargeable Batteries: Cobalt is a crucial component in lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles and electronic devices due to its ability to improve battery performance and stability.
5. Chemical Processing: Cobalt catalysts are employed in various chemical processes, such as petroleum refining, hydrogenation, and polymer production.
6. Industrial Tooling: Cobalt-based alloys are used in cutting tools, dies, and saw blades due to their high strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
7. Nuclear Industry: Cobalt alloys are used in nuclear reactors for control rods and other components due to their stability under radiation and high-temperature conditions.
8.Magnets: Cobalt is used to produce high-performance magnets, such as samarium-cobalt magnets and Alnico magnets, which are used in motors, generators, and sensors.
Our Cobalt Metals are clearly labeled for efficient identification and quality control. We take great care to prevent any damage during storage or transportation.

In the vast landscape of metals, one element stands out for its unique properties and versatile applications: cobalt. From its vibrant blue hue to its essential role in various industries, the world of cobalt metals is truly fascinating. With a maximum of 160 words, let’s take a journey to unravel the importance, uses, and impact of cobalt. As a brand voice is not provided, we will craft an engaging and informative introduction that captivates readers. Cobalt, often referred to as the “metal of the future,” has become an indispensable resource in modern society. Its remarkable strength and resistance make it a crucial component in aerospace engineering, defense technologies, and renewable energy systems. But it doesn’t stop there – cobalt is also a key ingredient in rechargeable batteries, electric vehicles, and even medical implants. Yet, as cobalt’s demand continues to soar, questions arise about its sustainability and ethical sourcing. Join us as we delve into the intricate world of cobalt metals, exploring its significance, countless applications, and the impact they have on our society and environment.
Cobalt’s significance in modern technology cannot be overstated. Its high melting point, magnetic properties, and ability to maintain its strength at high temperatures make it invaluable in many high-tech and industrial applications. As industries strive for more efficient and durable materials, cobalt’s unique characteristics position it as a critical component in innovation and technological advancement.
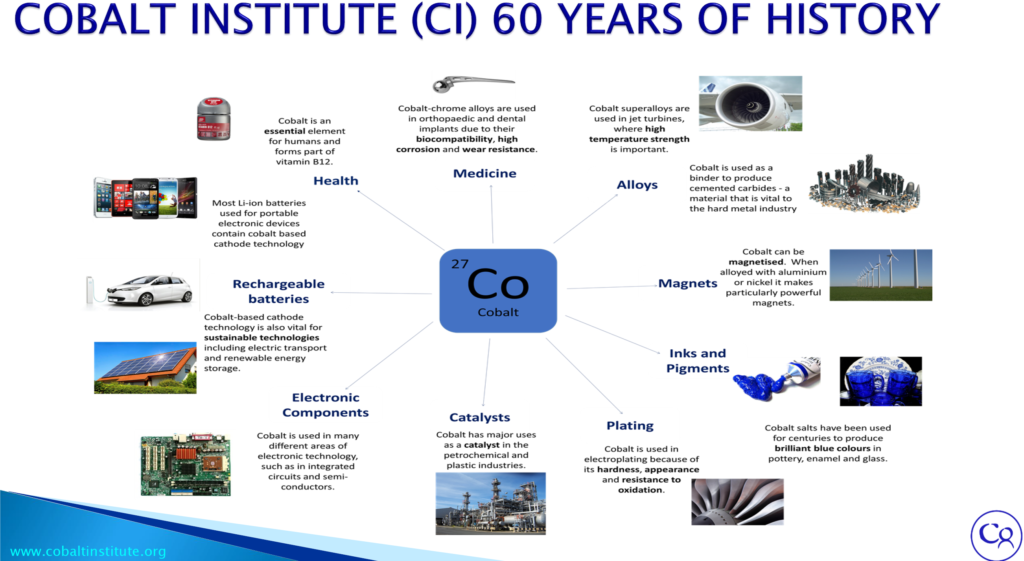
Cobalt metals find extensive applications across various industries due to their unique properties, including high melting point, corrosion resistance, and magnetic performance. Here are some key uses of cobalt metals in different industries:
Cobalt’s unique properties make it an essential raw material for various industries, contributing to advancements in technology, manufacturing, energy, and healthcare sectors.

Cobalt metals play a crucial role in various technology and electronics applications due to their unique properties. Here are some key uses of cobalt in the technology and electronics sectors:
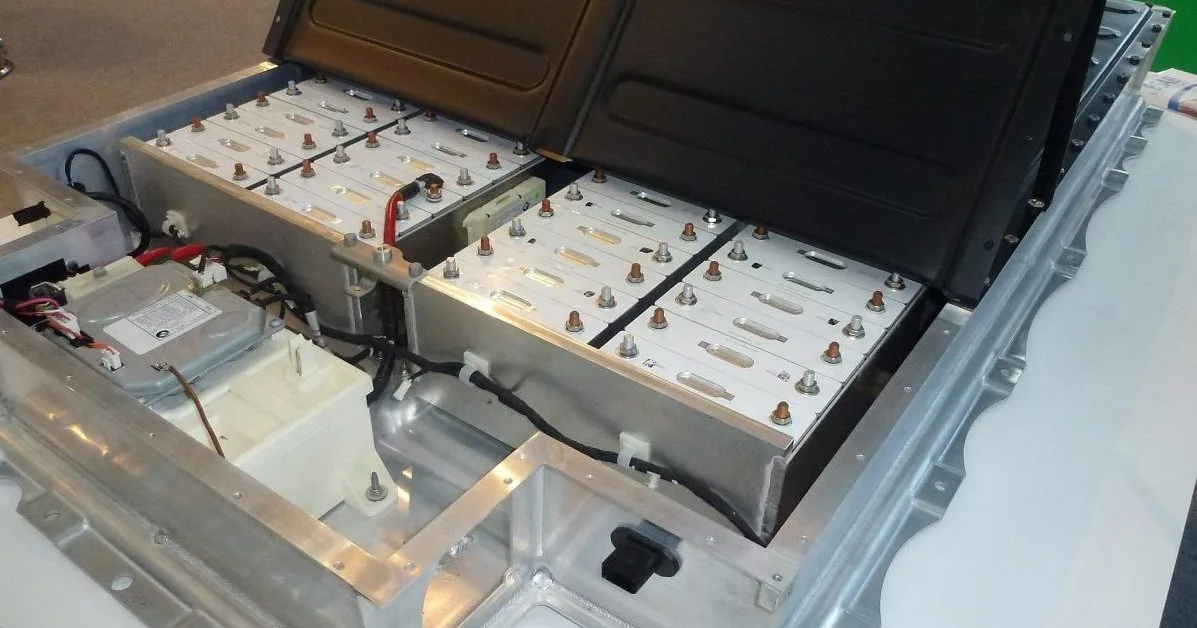

Cobalt’s unique properties, including high melting point, corrosion resistance, and magnetic performance, make it an essential raw material for various technology and electronics applications, contributing to advancements in energy storage, data storage, and electronic devices.
The growing demand for cobalt has brought attention to the environmental consequences of its extraction. Mining operations, particularly in regions like the Democratic Republic of Congo, have raised concerns about habitat destruction, water pollution, and carbon emissions. As the industry moves forward, there is an urgent need for more sustainable and environmentally friendly mining practices.
Cobalt mining and extraction processes have significant environmental impacts that raise concerns about sustainability and ethical practices. Here are some key environmental issues associated with cobalt mining and extraction:
While cobalt is an essential resource for many modern technologies, addressing the environmental and human health impacts of its mining and extraction is crucial. Efforts are underway to establish ethical supply chains, improve mining practices, and explore alternative sources or recycling methods to reduce the environmental footprint of cobalt production.

Cobalt metals play a crucial role in the medical and healthcare sectors due to their unique properties. Key applications include:
While beneficial, potential risks associated with cobalt exposure, such as implant wear or corrosion, must be considered. Ongoing research aims to optimize the safe and effective use of cobalt alloys in medical devices and treatments.
The future of cobalt metal applications looks promising, with ongoing research aimed at improving its efficiency and finding new uses. Advances in battery technology, particularly solid-state batteries, could further increase the demand for cobalt. Moreover, cobalt’s potential in emerging fields such as quantum computing and advanced manufacturing presents exciting opportunities for innovation.
Investing in cobalt metals presents both opportunities and risks. The increasing demand for cobalt in renewable energy and electric vehicles offers significant growth potential. However, market volatility, geopolitical issues, and ethical concerns surrounding cobalt mining can pose challenges for investors. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
Ethical and sustainable cobalt sourcing is crucial due to the environmental and social impacts associated with cobalt mining, particularly in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Key considerations include:Supply Chain Traceability and Due Diligence:
Responsible Sourcing Policies and Governance:
Artisanal and Small-Scale Mining (ASM) Formalization:
Multi-Stakeholder Collaboration:
Impact Monitoring and Remediation:
Responsible Sourcing Initiatives:
Ongoing efforts, collaboration, transparency, and a commitment to continuous improvement are crucial for companies to mitigate risks and drive positive change in the cobalt supply chain.
Cobalt metals remain integral to advancing technology and industry, driving innovations from aerospace to renewable energy. As we face the challenges of sustainable and ethical sourcing, MetalsTek stands at the forefront, offering high-purity, custom cobalt products that meet the highest standards of quality and responsibility. By partnering with MetalsTek, customers are assured of not only top-tier materials but also a commitment to ethical practices and environmental stewardship, ensuring that cobalt’s legacy continues to benefit society while preserving our planet for future generations.