Menu
MetalsTek Engineering provides high quality Tellurium Metals with competitive prices. We have Tellurium Metal in the form of powder, pieces, ingots and more.

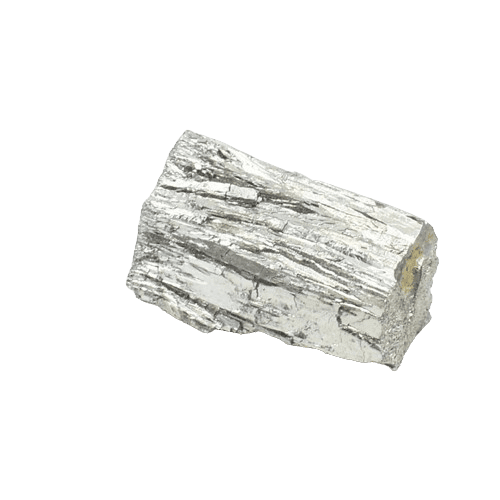
Material: Tellurium, 4N~7N
Purity: 99.99%, 99.999%, 99.9999%, 99.99999%
Particle Size: 100 ~ 500 Mesh, or Customized
CAS #: 13494-80-9

Material: Silver, Ag-99%
Temperatures: 961.78°C M.P., 2,162°C B.P.
Particle Size: 0.5~1μm
Surface Area: 0.4 to 1.5m2/g
Main Applications: Medical, Fabrics, Health Care, Electronic Paste, Catalyst
Tellurium is a relatively rare, heavy minor metal that finds its use in a variety of industries. It is commonly used in steel alloys and as a light-sensitive semiconductor in solar cell technology. Tellurium metal is crucial in the production of solar modules, sensors, and thermoelectric consumer appliances, such as water dispensers and vehicle coolers. It is also an essential component in electronics for storage modules and rewritable optical CDs, as well as in thermal imaging devices for infrared sensors.
In metallurgy, tellurium is used to enhance the properties of certain metals. For instance, it’s added to steel to improve its machine processing, to copper to improve workability while maintaining conductivity, to lead to enhance resistance against vibrations and material fatigue, and to cast iron to investigate hardness depth.
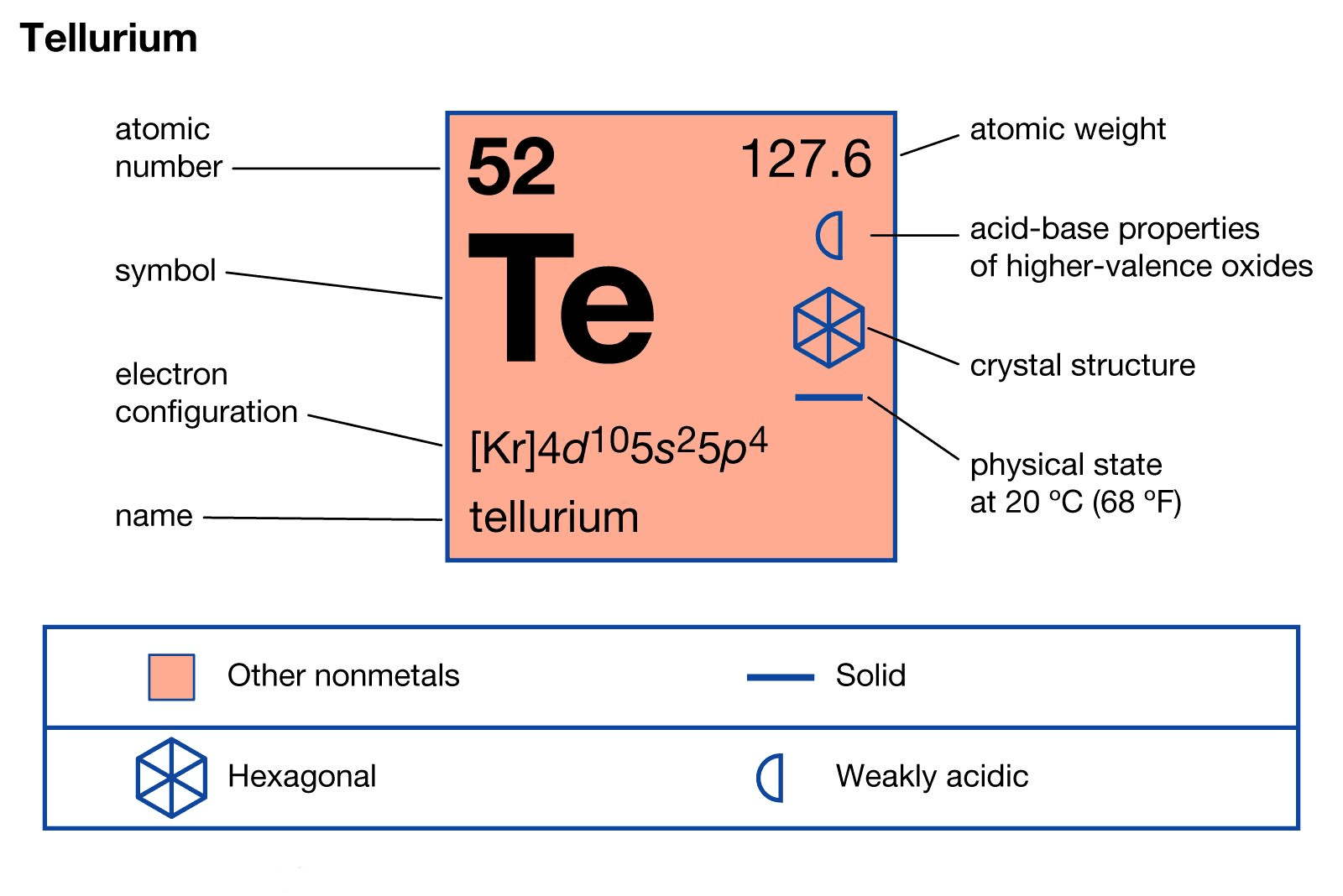
Tellurium is a semi-metal (metalloid) with silvery-white metallic appearance, although it is more commonly available as a dark grey powder. It is the 72nd most abundant element in the Earth’s crust. It is a member of Group 16 of the Periodic Table and has properties intermediate between metals and nonmetals. It is brittle, has poor electrical conduction, burns in air or oxygen, dissolves in nitric acid, and reacts with halogens to form halides.
Although tellurium can be found naturally in various minerals, it is mainly produced as a by-product of refining other metals, such as copper. The world production of tellurium is estimated at around 220 metric tons per year, with major mining regions including the USA, Canada, Peru, Russia, and Japan.
The future demand for tellurium looks promising, particularly in renewable energy sources like photovoltaic solar cells using cadmium telluride (CdTe). This has led to an increase in the demand for high-purity tellurium.
Material Type | Tellurium | Density | 6.25 g/cc |
Symbol | Te | Z Ratio | 0.9 |
Atomic Weight | 127.6 | Sputter | RF |
Atomic Number | 52 | Type of Bond | Indium, Elastomer |
Color/Appearance | Silvery Lustrous Gray, Semi-Metallic | UN Number | 3284 |
Thermal Conductivity | 3 W/m.K | Comments | Wets without alloying. Not recommended for sputtering. |
Melting Point | 449 °C |
Item No. | Description | Purity |
TE52-3N | Tellurium Metal Ingot, Chunks | 99.9% |
TE52-4N | Tellurium Metal Ingot, Chunks | 99.99% |
TE52-5N | Tellurium Ingot, powder, lump, particle, Semiconductor Applications | 99.999% |
TE52-6N | Tellurium Ingot, powder, lump, particle, Semiconductor Applications | 99.9999% |
TE52-7N | Tellurium Ingot, powder, lump, particle, Semiconductor Applications | 99.99999% |
Tellurium finds diverse applications across various industries, leveraging its unique properties to enhance products and technologies. Some key applications of tellurium include:
These applications highlight the importance of tellurium in advancing renewable energy, electronics, materials science, and various industrial sectors, contributing to innovation and sustainable development.
Our Tellurium Metals are clearly labeled externally to ensure efficient identification and quality control. To prevent any damage during storage or transportation, we take great care.