Menu
MetalsTek Engineering is a trusted supplier of Vanadium Carbide. We provide quality vanadium carbide in powder, micro powder, nano powder, and sputtering target.

Material: Vanadium Carbide, VC
Purity: 99.9% Min
Form: Micro Powder, Nano Powder, Spherical Powder
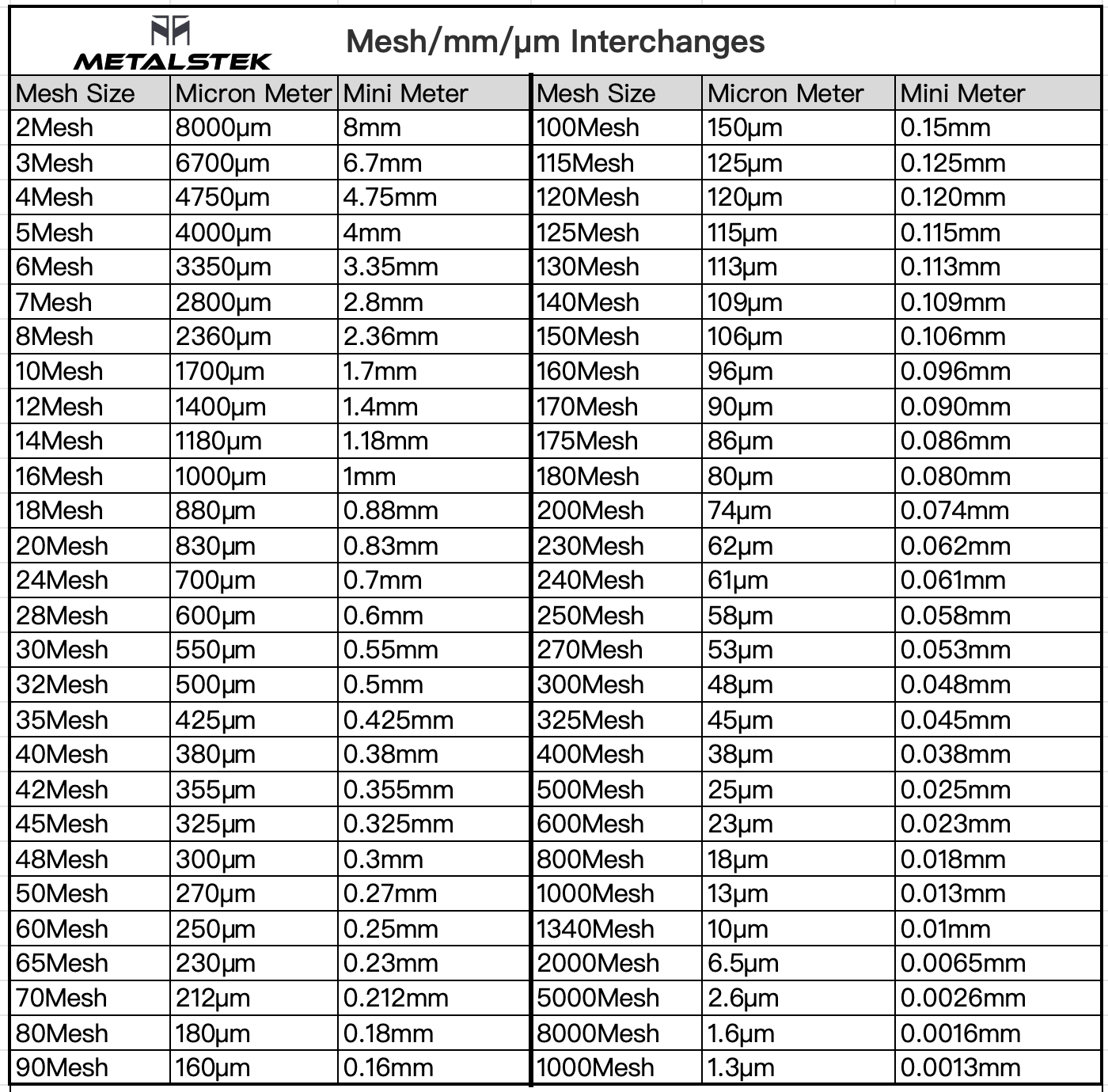
Particle Size: Nano Powder 100nm APS, 36 m2/g Surface Area
Micro Powder – 100μm~800μm APS
Melting Point: 2,810°C M.P.
Other: Size Can be Customized

Material: Vanadium Carbide, VC-99.5%, 99.9%
Properties: 3,608°C M.P., 5.77 g/cc
Form: Powder, Pieces, Pellets, Customized
Size: Tailored Sizes
Application: Optical Coating, Thin-Film Coating, Microelectronics, Aerospace

Material: Vanadium Carbide, VC
Purity: 99.5%, Can be Customized
Shape: Discs, Plates, Column Targets, Step Targets, Custom-made
Size: Round – Diameter < 14inch, Thickness > 1mm
Rectangular – Length < 32inch, Width < 12inch, Thickness > 1mm
Bonding: Indium, Elastomer
Vanadium Carbide (VC) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula VC. It is known for being an extremely hard and refractory ceramic material. With a hardness of 9-9.5 on the Mohs scale, Vanadium Carbide is considered one of the hardest metal carbides known. This makes it of significant interest for applications requiring high hardness and wear resistance.
Structure and Preparation
Vanadium Carbide crystallizes in the rock salt structure and is isomorphous with vanadium monoxide (VO), meaning it shares the same crystal structure. VC is typically produced by heating vanadium oxides with carbon around 1,000 °C. It can also be formed in the (111) orientation through radio frequency magnetron sputtering. However, at higher temperatures, VC is known to convert to V2C, another form of vanadium carbide.
Physical Properties
The elastic modulus of Vanadium Carbide is approximately 380 GPa, indicating its stiffness and resistance to deformation under stress. It has a lattice constant of 4.182 angstroms, a melting point of 2,800 °C, and a boiling point of 3,900 °C. These properties and their good chemical stability and high-temperature performance make Vanadium Carbide suitable for extreme environments.
| Grade | FXVC-01 | FVC-1 |
|---|---|---|
| Total Carbon | ≥17 | ≥16 |
| Free Carbon | ≤1.3 | ≤0.8 |
| N | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| O | 1 | 0.6 |
| Si | 0.1 | 0.15 |
| Fe | 0.1 | 0.15 |
| Na | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Ca | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Al | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| Fsss(μm) | ≤1.5 | 1.5<Fsss≤4.0 |
Vanadium Carbide is primarily used as an additive to cemented carbides, often used in tool bits and cutting tools. Adding VC refines the carbide crystals in these materials, leading to increased hardness and improved performance of the tools. It is also used in various other applications, including:
Our Vanadium Carbide Products are carefully handled to prevent damage during storage and transportation and to preserve the quality of our products in their original condition.