Menu
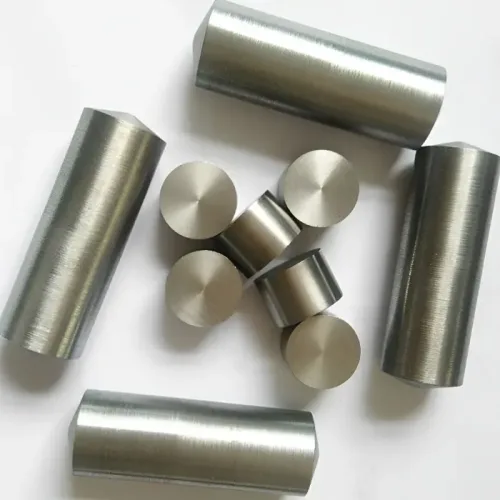





Material: Tungsten Heavy Alloys
Density: 15.8-18.75 g/cm3
Shape: Customized Shapes Tailored Sizes
Applications: Propeller Security Devices, Rivet Rods, Crankshafts, Aviation Use Satellites, Helicopters, Missiles, Gyroscopes, Oil Drills, Gyro Rotors, Azimuth Shafts, Military Shots, Shotgun Cartridges, Golf Counterweights, Prefabricated Fragments, Fishing Pendants, and More
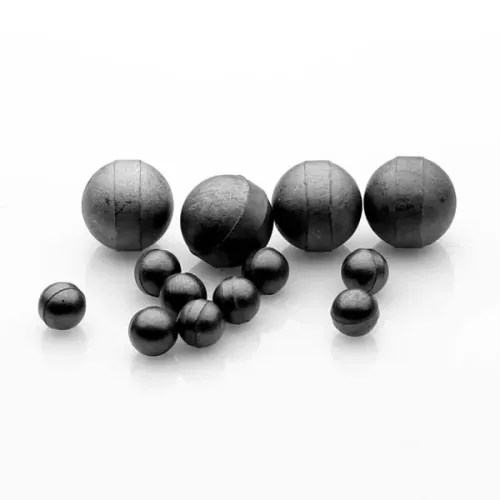






Material: W-Ni-Fe, W-Ni-Cu, or Customized
Composition: 85~99%
Density: 15.8-18.75 g/cm3
Size: Diameter 1~100mm
Application: Military Shots, Shotgun Cartridges, Golf Counterweight, Prefabricated Fragments, Fishing Pendants
Tungsten heavy alloys (WHA), particularly WNiFe, ballast weights are engineered for high density and excellent mechanical properties, making them ideal for various applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and defense.
WNiFe balls are spherical ballast weights made from a tungsten-nickel-iron alloy. They are known for their high density, which allows for compact designs without compromising weight. These spheres are often used in:
The manufacturing process involves sintering tungsten powder with nickel and iron to create a solid structure that withstands high temperatures and stresses.
WNiFe studs are elongated counterweights designed for applications where space is constrained. These studs offer similar properties to the spheres but are tailored for specific mounting or fastening needs. Common applications include:
The studs are produced using similar sintering techniques as the spheres, ensuring durability and performance under demanding conditions.
ASTM B777 (MIL-T-21014 / SAE-AMS-T-21014) is a standard specification for Tungsten Heavy Alloys (WHA). The specification is organized into four classes (1-4). Each categorization or classification represents a percentage amount of Tungsten (W) Alloy.
Class 1: W 90%
Class 2: W 92.5%
Class 3: W 95%
Class 4: W 97.5%
| Tungsten Heavy Alloy Grade | WHA-17C | WHA-17F | WHA-175 | WHA-18C | WHA-18F | WHA-185 |
| ASTM B777; AMS-T-21014 Class | Class 1 | Class 2 | Class 3 | Class 4 | ||
| Type | Type II & III | Type II & III | Type II & III | Type II & III | Type II & III | Type II & III |
| AMS 7725C | Type 1 | Type 2 | ||||
| Alloy Composition | 90WNiCu | 90WNiFe | 92.5WNiFe | 95WNiCu | 95WNiFe | 97WNiFe |
| 90% W | 90% W | 92.5% W | 95% W | 95% W | 97% W | |
| 6% Ni | 7% Ni | 5.25% Ni | 3.5% Ni | 3.5% Ni | 2.1% Ni | |
| 4% Cu | 3% Fe | 2.25% Fe | 1.5% Cu | 1.5% Fe | 0.9% Fe | |
| Density (g/cm3) | 17 | 17 | 17.5 | 18 | 18 | 18.5 |
| Density (lbs/in3) | 0.614 | 0.614 | 0.632 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.668 |
| Hardness (HRC) | 24~32 | 25~32 | 26~32 | 27~34 | 27~34 | 28~35 |
| Tensile Strength (PSI) | ≥94,000 | ≥110,000 | ≥110,000 | ≥94,000 | ≥105,000 | ≥100,000 |
| Yield Strength (PSI) 2% OFFSET | ≥75,000 | |||||
| Elongation, % in 1” | >2 | >5 | >5 | >2 | >3 | >2 |
| Proportional Elastic Limit (PSI) | 45,000 | 52,000 | 46,000 | 45,000 | 44,000 | 45,000 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (PSI) | 40 x 106 | 45 x 106 | 47 x 106 | 45 x 106 | 50 x 106 | 53 x 106 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion x 10E-6/°C (20°- 400°C) | 5.4 | 4.8 | 4.6 | 4.4 | 4.6 | 4.5 |
| Thermal Conductivity (cal/s*cm*K) | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.2 | 0.33 | 0.26 | 0.3 |
| Electrical Conductivity (%IACS) | 14 | 10 | 13 | 16 | 13 | 17 |
| Magnetic Properties | NIL | Slightly Magnetic | Slightly Magnetic | NIL | Slightly Magnetic | Slightly Magnetic |
There are many different ways to use Tungsten heavy alloy (WHA). Mostly, we provide WHA parts for ballast weights, radiation shields, boring bars, ordnance components, and other things that need to be really heavy and flexible.
WHA is commonly used in various applications, such as counterweights, inertial masses, radiation shielding, and ordnance products. It is preferred for its strength, density, and weight, making it suitable for applications that require balance weights, such as turbines, crankshafts, and helicopter rotors.
WHA is also used in commercial and military aircraft, spacecraft, defense vehicles, transportation systems, warheads, munitions, and fragmentation.


In the medical industry, WHAs are used for X-ray shielding in applications such as CT and imaging technologies, nuclear medicine shielding, and surgical robots. The alloying of tungsten allows for the production of complex shapes and forms needed for critical medical devices and technologies.
Below are the typical uses of WHA:
Our Tungsten Heavy Alloy products are meticulously tagged and externally labeled, ensuring both efficient identification and rigorous quality control. We prioritize utmost care to prevent any potential damage that may occur during storage or transportation.