Menu
Tungsten crucibles and other parts can be used for sapphire crystal growth and rare-earth melting due to their high-temperature resistance, low pollution, and other excellent characteristics. Tungsten’s melting point is 3,422°C (6,192°F), making it perfect as a crucible.
MetalsTek Engineering is a leading supplier of Tungsten Crucibles, including E-Beam Crucibles, Standard Crucibles and Custom Crucibles. We offer competitive pricing and excellent lead times on Tungsten Crucibles, and we can supply custom materials per any specs/drawings you provide.
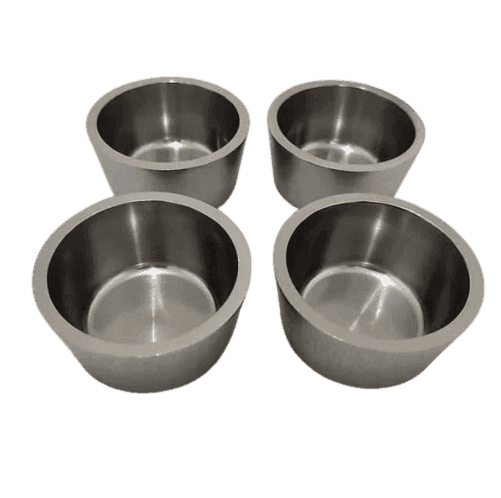

Material: Tungsten, W 99.95%
Shape: Arc, Square, Rectangle, Cylinder, Boat
Outer Diameter: ≤200mm / Height: ≤500mm
Deposition thickness: ≤10mm
Standard Capacities: 1mL ~ 40mL, Can be Customized
>Custom sizes are available upon request.
>Recommended for chrome evaporation.
>Refractory metal crucibles can be good alternatives to other carbon-based crucibles where there are concerns about trace carbon contamination.

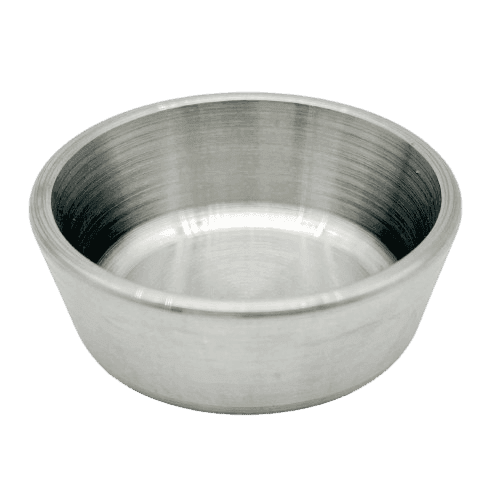
Material: Tungsten, W≥99.95%
Density: ≥18.2g/cm3
Surface: Ra≤1.6
Operating temperature: ≤2,400 Degree C
Size: Customized Sizes
Production method: Sintered (OD>70mm); Forged (OD<70mm)
Other: With or Without Lid
Material: Tungsten or Tungsten Alloy
Purity: 99% ~ 99.9999%
Outer Diameter: ≤200mm
Height: ≤500mm
Deposition thickness: ≤10mm
Other: Tailored Shape, Tailored Sizes

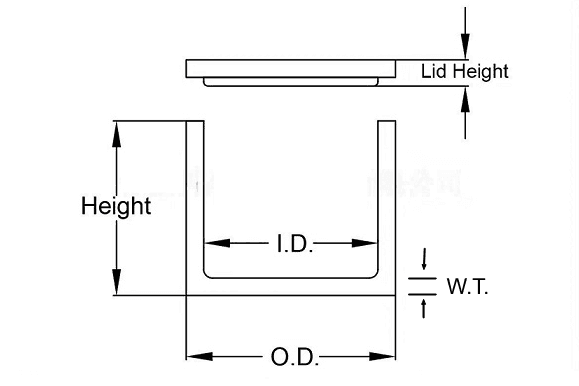

| Outer Diameter (mm) | Wall Thickness (mm) | Height (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 ~ 30 | 1.0 ~ 3 | 20 ~ 50 |
| 30 ~ 50 | 2~ 10 | 20 ~ 100 |
| 50 ~ 100 | 3 ~ 15 | 30 ~ 150 |
| 100 ~ 150 | 3 ~ 15 | 30 ~ 500 |
| 150 ~ 200 | 5 ~ 20 | 30 ~ 500 |
| 200 ~ 300 | 8 ~ 20 | 30 ~ 500 |
| 300 ~ 400 | 8 ~ 30 | 40 ~ 500 |
| 400 ~ 450 | 8 ~ 30 | 50 ~ 500 |
| 450 ~ 620 | 8~ 30 | 50 ~ 500 |
| Shape and size can be tailored. Rectangular tungsten crucible is available. | ||
Tungsten crucibles and other parts can be used for sapphire crystal growth and rare-earth melting due to their high-temperature resistance, low pollution, and other excellent characteristics. Tungsten’s melting point is 3422°C (6192°F), making it perfect as a crucible.
The tungsten crucibles manufactured through the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process exhibit notable characteristics, including a high density reaching up to 98.5% of theoretical density, exceptional purity at 99.9999%, and a distinctive microstructure characterized by columnar or multilayer columnar crystals.
These tungsten crucibles find widespread applications in the production of monocrystals from molten corundum and play a vital role in electronics and thermal vaporization technologies for depositing various substances. Their high melting point is a key attribute of high-temperature furnaces.
Our tungsten crucibles are distinguished by their outstanding thickness transition, smooth surface, high purity, and robust resistance to creep, making them well-suited for demanding applications in high-temperature environments.
Tungsten crucibles find versatile applications across various industries due to their unique properties. Here are some common applications of tungsten crucibles:
Our Tungsten Crucibles are clearly tagged and labeled externally to ensure efficient identification and quality control. Great care is taken to avoid any damage which might be caused during storage or transportation.
Imagine a material that can withstand temperatures so extreme that most metals would melt into a pool of liquid. This isn’t the stuff of science fiction—it’s the reality of tungsten crucibles. Used across high-tech industries, from aerospace to electronics, tungsten crucibles are essential for processes that push the limits of heat and harsh environments.
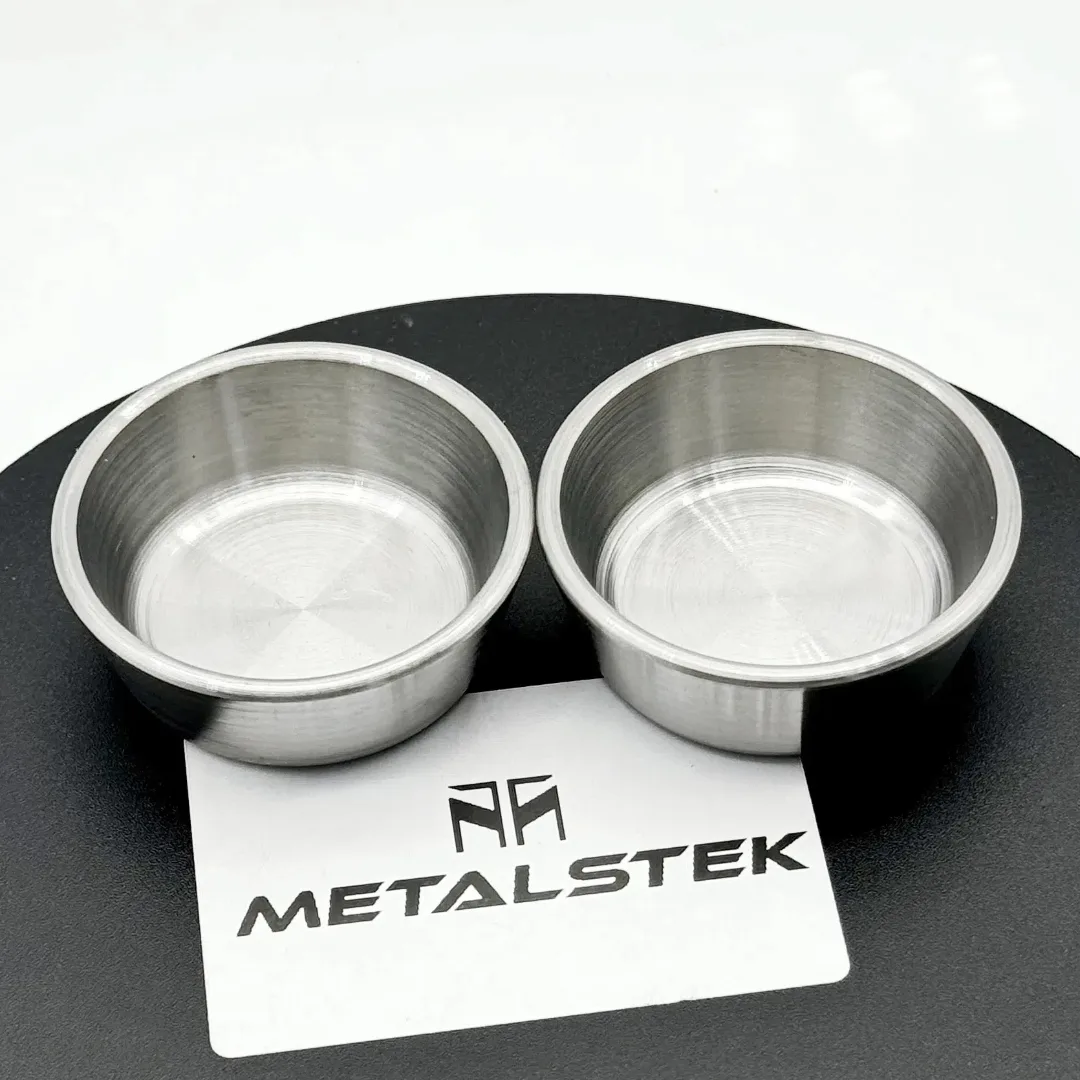

A tungsten crucible is a specialized container crafted from tungsten, known for its exceptional properties, particularly its high melting point, which is the highest of all metals at 3422°C (6192°F). This makes tungsten crucibles incredibly valuable for industries and applications that require materials to be heated to extreme temperatures. Their ability to withstand such conditions without melting, deforming, or contaminating the contents makes them essential in various high-tech, scientific, and industrial processes.
Tungsten itself is a dense, hard metal with excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, and remarkable resistance to corrosion and wear. These properties are critical because they allow the crucible to perform under stressful conditions, including high heat, corrosive environments, and mechanical wear. The material’s high density and mechanical strength also contribute to its effectiveness in containing heavy or aggressive substances securely.
The main appeal of tungsten crucibles lies in their performance in high-temperature applications, where lesser materials would fail. They are used extensively in fields such as semiconductor manufacturing, metallurgy, and materials science, especially for tasks like melting rare metals, growing crystals for electronics and optics, and performing heat-based chemical reactions and analyses.
Overall, tungsten crucibles represent a pinnacle of material engineering, combining durability, efficiency, and purity to meet the demands of cutting-edge technological processes. They are an indispensable tool for researchers and industries pushing the limits of what’s possible with modern materials technology.

Tungsten can be a crucible material because of its specific properties, which include:
Tungsten crucibles are designed to meet the specific requirements of various high-temperature processes, making them indispensable in several advanced applications. Depending on the specific use and the unique demands of each application, different types of tungsten crucibles are utilized. Here’s a look at some of the primary types of tungsten crucibles available:
These are the most commonly used tungsten crucibles and are typically cylindrical in shape. Standard tungsten crucibles are used in a wide range of applications from melting metals and alloys to chemical analysis. Their robustness and high melting point make them suitable for general purposes in laboratories and industrial settings.
E-beam crucibles are specifically designed for use in electron beam evaporation systems. These systems are crucial in the thin film deposition processes used in the manufacturing of semiconductors and solar panels. E-beam crucibles often have a more complex design to accommodate the precise requirements of electron beam targeting and evaporation rates, ensuring efficient and uniform material deposition.
For specific applications, tungsten crucibles can be custom-made to various shapes and sizes. This customization allows them to fit perfectly within particular equipment or to optimize the performance for specific processes. For example, crucibles tailored for growing sapphire crystals for LED applications may have unique geometries that optimize the heat distribution and material handling.
These crucibles are made from denser tungsten to provide additional strength and durability. High-density tungsten crucibles are particularly useful in processes that require exceptional thermal conductivity and robustness, such as in high-temperature sintering or melting of particularly abrasive or corrosive materials.
For applications requiring extremely high purity, such as certain chemical reactions or materials processing in the semiconductor industry, crucibles can undergo special chemical cleaning processes. This treatment ensures that there are no contaminants that could potentially interfere with the processes or compromise the quality of the final products.
In some extreme cases, tungsten crucibles are reinforced with other materials to enhance their performance. This might include coatings or linings of other refractory metals that can provide additional resistance to chemical attack or thermal shock.
Each type of tungsten crucible is designed with a specific set of applications in mind, reflecting the diversity of requirements in various fields that rely on high-performance materials under challenging conditions. The choice of a particular type of tungsten crucible depends on factors such as temperature requirements, chemical exposure, and physical stress levels, ensuring that the crucible can perform optimally within its intended environment.
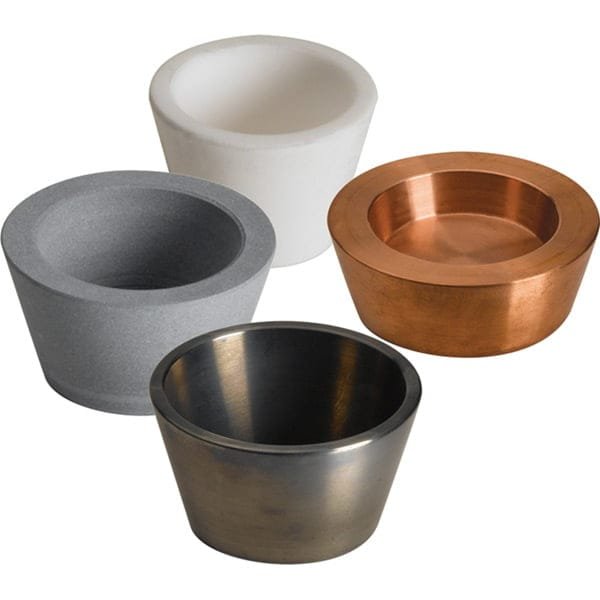

Tungsten crucibles offer a combination of outstanding properties that make them indispensable in various high-technology, industrial, and scientific applications. Here’s a detailed look at what tungsten crucibles are used for, along with their key advantages.
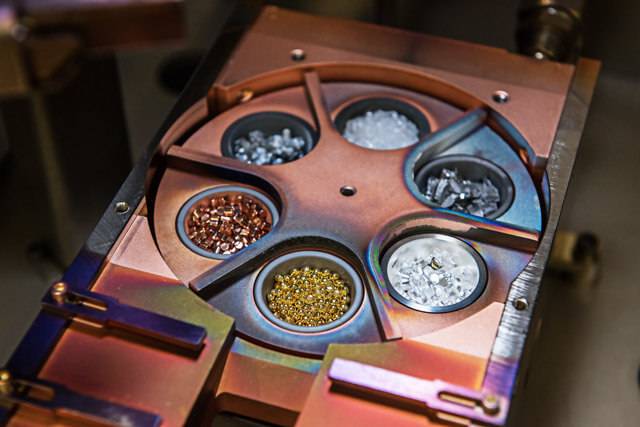


Choosing the right tungsten crucible for your specific application involves understanding several key factors that affect performance, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Here’s a detailed guide to help you make an informed decision:
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a tungsten crucible that meets your needs effectively, ensuring optimal performance and durability in your high-temperature applications.
Despite their advantages, tungsten crucibles present challenges such as their high cost and the difficulty in machining due to their hardness. Proper maintenance can help extend their lifespan, avoiding rapid temperature changes to prevent thermal shock, and handling with care during installation are critical for maximizing their use.
Tungsten crucibles play a pivotal role in the advancement of materials technology, offering unmatched performance in high-temperature applications. Industries that require utmost reliability and precision under extreme conditions would do well to consider tungsten crucibles as a key component of their manufacturing processes. As technology continues to evolve, the demand for such resilient materials will only grow, making the investment in tungsten crucibles a wise choice for future-ready industries.
At MetalsTek, we take great pride in providing top-notch Tungsten Crucibles that meet the demanding requirements of today’s industries. Our dedication to quality, coupled with our capability to tailor targets to precise sizes and compositions, positions us as the go-to choice for businesses looking to push boundaries and achieve greatness.