
Titanium alloys are among the most sought-after materials in industries like aerospace, medical, and industrial manufacturing due to their exceptional strength, corrosion resistance, and lightweight properties. Among them, Titanium Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) and Grade 23 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI) stand out as two of the most commonly used.
But what’s the difference between Titanium Grade 5 and Grade 23? Which one should you choose for your project? In this guide, we’ll break down their chemical composition, mechanical properties, applications, and key differences, helping you make the right choice for your needs.
What Are Titanium Grade 5 and Grade 23?

Both Grade 5 and Grade 23 have the same base composition:
✅ 90% titanium
✅ 6% aluminum
✅ 4% vanadium
The main distinction lies in Grade 23’s Extra Low Interstitial (ELI) content, which means it has lower levels of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and iron. This makes Grade 23 more ductile, fracture-resistant, and biocompatible than Grade 5.
- Titanium Grade 5 is the industry’s workhorse, providing a great balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and machinability.
- Titanium Grade 23 is a more refined version of Grade 5, with better biocompatibility, fatigue resistance, and weldability, making it the preferred choice for medical implants.
**See our full range of Titanium Products.
Key Differences Between Titanium Grade 5 and Grade 23
Comparison of Titanium Grade 5 and Grade 23 Mechanical Properties
| Property | Titanium Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) | Titanium Grade 23 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI) |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Ti-6Al-4V | Ti-6Al-4V with lower oxygen, nitrogen, and iron |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS) | ~1000 MPa (145 ksi) | ~900 MPa (130 ksi) |
| Yield Strength | ~880 MPa (128 ksi) | ~830 MPa (120 ksi) |
| Elongation (%) | ~10% | ~15% (higher ductility) |
| Fracture Toughness | Standard | Higher fracture resistance |
| Fatigue Strength | Good | Superior fatigue resistance |
| Biocompatibility | Moderate | Excellent (Preferred for medical use) |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Slightly better due to lower interstitials |
| Machinability & Weldability | Moderate | Better machinability & weldability |
| Common Applications | Aerospace, automotive, marine, industrial machinery | Medical implants, dental implants, surgical devices |
🔹 Strength & Mechanical Properties
- Grade 5 has higher tensile and yield strength, making it ideal for aerospace and industrial applications where high loads are involved.
- Grade 23 has improved ductility and fracture toughness, which is crucial for medical implants that require high fatigue resistance.
🔹 Corrosion Resistance & Biocompatibility
- Both grades exhibit excellent corrosion resistance in extreme environments.
- Grade 23 is superior in biocompatibility, making it the preferred choice for surgical implants like hip and knee replacements.
🔹 Machinability & Weldability
- Grade 5 is harder to machine due to its slightly higher oxygen content.
- Grade 23 is easier to weld and shape, making it more versatile in delicate applications.
Applications: Where Are They Used?
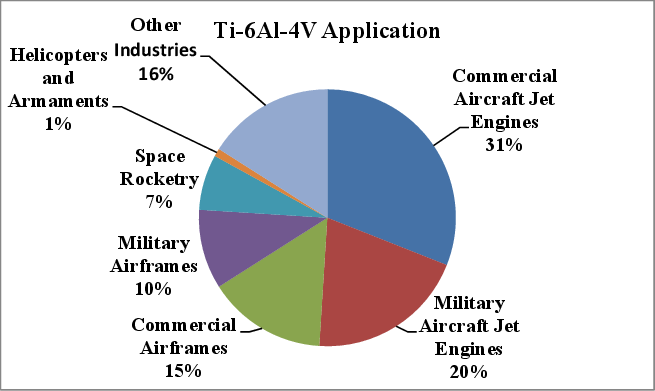
Titanium Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V) Applications
✔ Aerospace components (airframes, landing gear, jet engines)
✔ Industrial machinery (offshore drilling, power plants, chemical processing)
✔ Automotive (performance car parts, exhaust systems, suspension)
✔ Sports equipment (bicycles, golf clubs, racing parts)
Discover how Titanium Grade 5 is used in aerospace.
Titanium Grade 23 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI) Applications
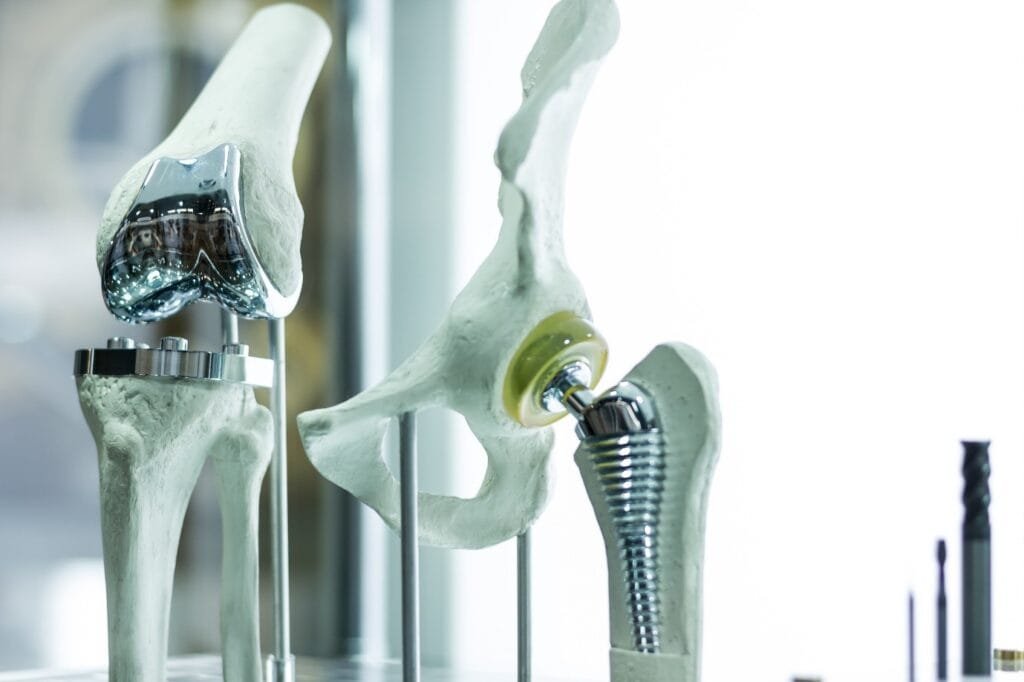
✔ Medical implants (hip and knee replacements, bone plates, spinal implants)
✔ Dental implants (screws, crowns, abutments)
✔ Surgical tools and orthopedic devices
✔ Cryogenic applications (low-temperature environments like liquid gas storage)
Other Common Titanium Alloy Grades
Besides Grade 5 and Grade 23, several other Titanium Alloys serve different industrial and medical purposes.
🔹 Grade 1-4 (Commercially Pure Titanium)
- High corrosion resistance, moderate strength
- Used in marine, chemical processing, and medical devices
🔹 Grade 7
- Similar to Grade 2 but with added palladium for superior corrosion resistance
- Used in nuclear power plants and aggressive chemical environments
🔹 Grade 9 (Ti-3Al-2.5V)
- Excellent weldability and strength, commonly used in marine and aerospace applications
- Found in bicycle frames and high-performance exhaust systems
🔹 Grade 12
- Resistant to high-temperature corrosion, ideal for chemical processing and power generation
🔹 Beta Titanium Alloys (Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al, Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr)
- Used in aerospace and high-performance automotive applications due to their high strength and toughness
Which One Should You Choose?
✅ Choose Titanium Grade 5 if:
✔ You need high strength and durability for aerospace, industrial, or structural applications
✔ Your project doesn’t require extreme ductility or biocompatibility
✔ You are working in offshore, automotive, or sports equipment manufacturing
✅ Choose Titanium Grade 23 if:
✔ Your application requires medical-grade biocompatibility (e.g., implants, surgical devices)
✔ You need higher fracture resistance and better fatigue strength
✔ You are working with cryogenic applications or lightweight marine structures

Final Thoughts
Both Grade 5 and Grade 23 are exceptional titanium alloys that offer superior performance in demanding applications. While Grade 5 excels in aerospace and industrial sectors, Grade 23 dominates in medical and biomedical applications.
Choosing the right titanium grade ensures long-lasting performance, cost-effectiveness, and safety in your industry.
Get High-Quality Titanium from MetalsTek!
At MetalsTek, we specialize in high-purity titanium materials for aerospace, medical, and industrial applications. Contact us today for:
✅ Custom titanium alloys
✅ Machining and fabrication services
✅ Bulk orders and OEM solutions
📩 Email us at sales@metalstek.com
🌎 Visit us at www.metalstek.com
👉 Need a quote? Get in touch now!
